Your ultimate guide to intermittent fasting
Share on facebook
Facebook
Share on twitter
Twitter
Overview
Intermittent fasting is the current trending method for improving health and losing weight because of its simplicity and affordability. For those of us that have grown up hearing that breakfast is the most important meal of the day, the idea of not eating until noon might raise some eyebrows, but according to the New England Journal of Medicine, there are several health benefits to skipping a few meals, including increased stress resistance, increased longevity, and decreased incidences of diseases like cancer and obesity.
Health Deal gives you the 101 on the various methods of intermittent fasting as well as its benefits and side effects.
What is intermittent fasting
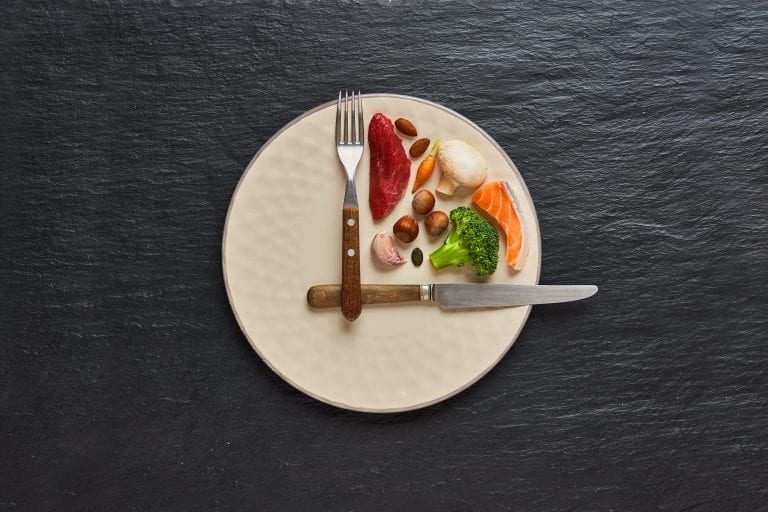
The concept of intermittent fasting is simple. If you normally have breakfast at around 7 am and end with dessert at around 9 pm, think of all the meals in between- you’ve been eating for around 14 hours. Those 14 hours is your eating window. Intermittent fasting is simply the process of reducing that eating window to trigger a metabolic switch from glucose to ketone-based energy.
Why is intermittent fasting so popular?
What is so appealing about fasting for weight loss is the added benefit of being able to eat whatever you want (within reason); it only asks that you hold off eating it for a few hours. You don’t need to buy any supplements or special meals and as the days go by it actually becomes easier to execute because your body becomes accustomed to your new eating pattern. It’s simple enough for anyone to do, but it has enough benefits to warrant a difference in your body.
How does it work?
First, you need to understand what happens to your body when it is experiencing the two phases of the digestive system: the fed state and the fasted state.
When we eat, our bodies produce and release insulin hormones, even more so when we consume refined food like carbohydrates. Almost all food stimulates production of insulin, with the exception of pure fat, which releases none at all.
In the fed (or absorptive) state, your body digests food for up to 4 hours. During this time, your insulin levels are elevated, prompting your body to store any excess calories in the fat cells. Elevated insulated levels also stop your body from burning fat and instead rely on glucose for energy.
So, when your body is in the fed state, it is extremely hard for it to burn any fat because of your high insulin levels.
The fasted (or post-absorptive) state starts 12 hours after our last meal, allowing our body to burn fat much easier because of its low insulin levels. The fasted state allows the body to access and burn the fat that it could not during the fed state, which is what normally triggers weight loss during fasting regardless of what and how much they eat.
Benefits of intermittent fasting
The great thing about intermittent fasting is being able to lose weight and still eat what you like. Intermittent fasting doesn’t require you to cut out any sugar or carbs (although reducing these things would speed up weight loss), but there are many other benefits to intermittent fasting such as this one, which you probably didn’t think about:
You save money on food
Many people who have tried intermittent fasting discover an almost accidental bonus- they save money on food. Because you’re only eating two meals per day, you’re buying less food. You also cut out the impulse eating and snack purchases, as well as avoiding food wastage. Some intermittent fasters report that they save around $100 a month- that’s $1,200 a year- the cost of a mini-vacation or a whole new wardrobe.
Increases your mental function
When your body becomes accustomed to your new eating schedule, your blood sugar levels stabilize early in the day and begin to burn fat for fuel. This provides your brain with constant energy, improved focus, and clarity. Intermittent fasting may also be linked to the growth of neurons, which can help protect the brain against damage.
Easy and simple
Most diets are easy to begin and then get harder as you go along. Not only do most people find it easy to adjust to their new eating pattern relatively easily, but it also simplifies meal planning and doesn’t require additional programs or supplements.
Lowers your risk of diabetes
Because you’re reducing your insulin resistance and your blood sugar levels, you’re also lowering your risk of type 2 diabetes, which has become increasingly common in the past decades.
Studies have found that those who participate in intermittent fasting reduce their blood sugar levels by 3-6% and insulin levels dropped by 20-31%.
Triggers cellular repair
Autophagy is the body’s way of flushing out damaged cells to allow regeneration to take place. Fasting triggers the removal of waste from to make way for healthy, new cells.
Studies show that increased autophagy may be linked to decreasing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, and some cancers.
Aids longevity
Perhaps one of intermittent fasting’s greatest benefits is its ability to lengthen your life span. Although studies on humans are still ongoing, other research has found that fasting can aid longevity.
With the prompting of waste removal and new cell growth, improved brain function, and the health merits of keeping your weight down, intermittent fasting improves your overall health and increases your chances of living longer.
Side effects of intermittent fasting
While there are great benefits to intermittent fasting, there are also side effects. Children, pregnant and nursing women, and diabetics should not practice intermittent fasting. Those with chronic conditions or eating disorders should consult their doctors before attempting fasting. People who find that fasting interferes with their daily responsibilities, are often dizzy, or begin to have an unhealthy obsession with food should see their local GP for advice.
Hunger
You will likely experience hunger when you first give intermittent fasting a go. This is the most obvious side effect because if you’re used to eating several times a day, your body will have become accustomed to that pattern of eating. The good news is, your body can adjust to two meals just as quickly, and you can have as much black coffee and water as you like- two things that are known for curbing hunger. It is also important to get your fill of healthy fats, carbohydrates, and protein the day before.
Cravings
When you think about food, you will likely be craving sugar and refined carbs because your body is looking for a hit of glucose. When the sugar bug hits, try to drink water, do something to occupy yourself and be sure to give yourself a little treat when your eating window opens so you can satisfy your cravings.
Increased trips to the convenience
This is an unavoidable side effect of intermittent fasting as you’re hydrating more often to last until your next eating window.
Types of intermittent fasting
16:8 Diet
This type of fasting is also known as the Leangains Protocol and was introduced by Swedish nutritionist, Martin Berkhan. It involves fasting for 14-16 hours and limiting your eating window to 8-10 hours.
The advantage of this fast is that you can eat your last meal at 8 pm and have your first meal at noon. Basically, you’re only skipping breakfast and half of your fasting hours are spent sleeping. While this method may prove difficult for those that enjoy a hearty breakfast, if you habitually skip breakfast, this method of fasting won’t be much of a challenge.
The 5:2 Diet
The 5:2 diet was invented by the gut health guru Michael Mosley and is a pretty simple concept that is more of a lifestyle than a diet. Essentially, for five days a week, you follow your regular eating schedule and then for two days you restrict your calorie intake to around 500-600 calories per day.
If you’re fasting for weight loss using the 5:2 diet, bear in mind you don’t overcompensate for your sugar and carbs on your 5 days by binge eating and consuming a lot of junk.
Alternate-Day Fasting
This involves fasting every other day, usually with an allowance of 500 calories during the fasting days. This can become uncomfortable for those unaccustomed to fasting, so it is not a recommended method for beginners who will feel the side effects of intermittent fasting much more acutely.
The 24 Hour Fast
Basically, this involves fasting from dinner one day until dinner the next day. You can do this fast with any of your meals.
During the fasting periods, you can have as much coffee and water as you want. If you’re fasting for weight loss, you mustn’t binge on junk food and overeat on your eating days.
Fasting beginners may want to reduce their fasting hours and work their way up to 24 hours to avoid feeling ravenously hungry and breaking fast early.
The Warrior Diet
One of the first intermittent diets to become popular was the Warrior Diet, which involves eating small serves of raw fruits and vegetables during the day and then eating a full dinner during your 4-hour eating window.
Intermittent fasting FAQs
Can I drink liquids during fasting?
Yes, as long as it is a non-calorific beverage such as water, black coffee or tea. You shouldn’t add sugar, artificial sweeteners but you can add a small splash of milk or cream, as long as it stays below 50 calories to keep your body in the fasted state.
Can I exercise during fasting?
Yes, this is fine, and many studies even state that one of the benefits of pairing intermittent fasting with exercising is that you become more sensitive to insulin and allow the human growth hormone to assist you in burning fat and muscle
Can fasting result in muscle loss?
Another benefit of intermittent fasting is that unlike other diets, you don’t lose muscle mass while losing weight. The key to maintaining muscle mass is ensuring that your eating window includes high-quality protein
Does my metabolism slow down fasting?
No. Research reveals that short term fasting boosts your metabolism however one of the side effects of extended fasting (3 days or more) is a slow metabolism.
Lifestyle Changes
When making lifestyle changes, you will be adjusting your pattern of eating, daily activities, and making any necessary changes to your home and work. An often overlooked particular that needs to be reviewed regularly is your health insurance policy. Contact Health Deal today for a free, unbiased, and obligation-free health insurance comparison.
I feel completelely confident about my switchJulie Read More
I received a much better deal!
All of my questions were answered and clarified and I feel completely confident about my health insurance switch.
I thoroughly recommend others to make use of this opportunity to simplify the entire process.

Would you like us to help you find the perfect health insurance plan?
Click here to compare
Top 10 New Year’s resolutionsyour doctor will thank you for Read Here A quick guideto breast self-screening and mammograms Read here
Previous
Next






 Single
Single Couple
Couple Family
Family Single Parent
Single Parent